Argon Plasma Coagulation
Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC)
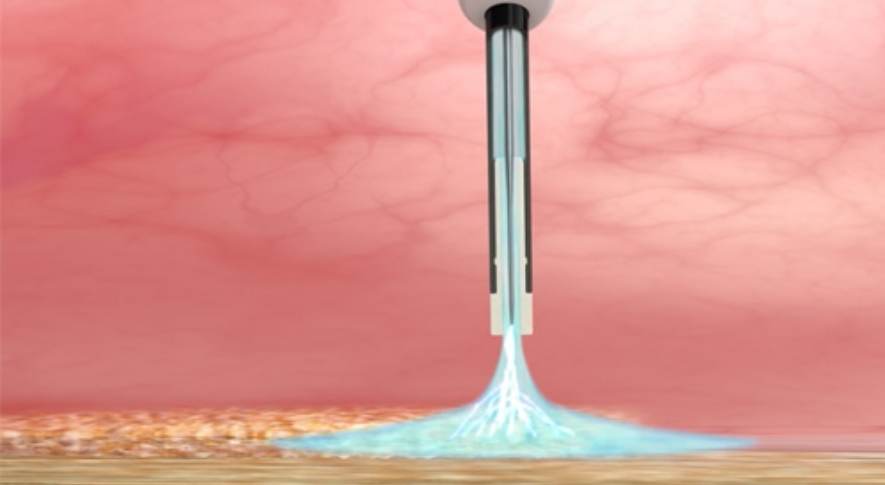
Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC) is a medical endoscopic procedure used to control bleeding caused by certain lesions in the gastrointestinal system and to shrink tumors for which surgery is not recommended. APC involves the use of ionized argon gas (plasma) jet directed through a probe passed through an endoscope.
Contents
- -Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC)
- -Why is Argon Plasma Coagulation Done?
- -Applications of Argon Plasma Coagulation Procedure
- -Advantages of the Procedure
- -Side Effects and Complications
- -How is Argon Plasma Coagulation Done?
Argon plasma coagulation is a coagulation method used in gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures. It is used to achieve hemostasis (stop bleeding) and treat lesions.
APC is based on the principle of delivering electrical energy to the target tissue using argon gas. This causes vaporization of water in the tissue, leading to coagulation, thus stopping bleeding or treating lesions.
Why is Argon Plasma Coagulation Done?
The procedure is used to treat various conditions in the gastrointestinal system:
- - Control of Bleeding: APC can rapidly stop gastrointestinal bleeding. It is particularly effective in bleeding from vascular lesions such as ulcers, angioectasias.
- - Treatment of Lesions: APC is used in the ablation (destruction) of certain lesions such as residual polyps, Barrett's esophagus.
- - Treatment of Residual Tissue: It is an effective method for treating residual tissue after endoscopic resection.
- - Prophylaxis: APC can also be used in the prophylactic treatment of lesions at risk of bleeding. This is particularly relevant for small vascular lesions in high-risk areas.
Applications of Argon Plasma Coagulation Procedure
- - Treatment of active gastrointestinal bleeding
- - Coagulation of vascular lesions
- - Treatment of residual adenoma tissue
- - Ablation therapy for Barrett's esophagus
Advantages of the Procedure
- - It does not penetrate deep tissues, hence the risk of complications is lower.
- - It is fast and effective for hemostasis.
- - It offers a more controlled treatment compared to other coagulation methods.
Side Effects and Complications
Like any medical procedure, APC has potential side effects. These may include perforation, bleeding, infection, and formation of burns. However, with proper technique and experienced hands, these risks are minimal.
Argon Plasma Coagulation is an effective method for the treatment of bleeding and certain lesions in gastroenterology. However, it is essential that the procedure be performed under the supervision of an experienced endoscopist to be successful and safe.
How is Argon Plasma Coagulation Done?
The Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC) procedure is performed using a specialized device and endoscope. The basic steps of the procedure are as follows:
- - Preparation: Local anesthesia or sedation may be applied depending on the patient's condition. This ensures the patient remains comfortable and still.
- - Advancement of Endoscope: The endoscope is advanced to the desired area with the assistance of a probe connected to the APC device.
- - Application of Argon Gas: The APC device releases a thin flow of argon gas out of the tip of the endoscope. This gas fills the space between the electrode and the tissue, creating electrical conductivity.
- - Coagulation: When electrical current is applied, the argon gas turns into plasma. This plasma delivers energy to the tissue, resulting in coagulation (searing) of the tissue. Coagulation occurs only on the surface, minimizing deep tissue damage.
- - Completion of the Procedure When the necessary coagulation is completed, the device is turned off, and the endoscope is carefully removed.
ENDOSCOPY/COLONOSCOPY
ENDOSCOPIC OBESITY
ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY
ENDOSCOPIC REFLUX PROCEDURES